Fungal diseases of the skin are called “cutaneous mycoses”. These infections in the surface layer of the skins (stratum corneum) that normally do not penetrate to deeper levels of the organism.
Depending on the location, skin, nails, scalp, mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, etc., adopt an appearance or another.
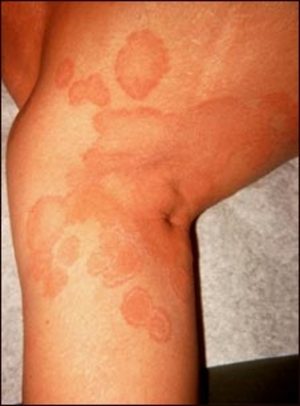
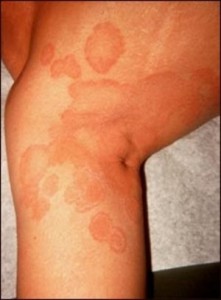
These infections are more common in humid areas of the body surface, since moisture encourages the growth of fungi, under the breasts, underarms, etc.., and are, in turn, more frequent in obese people with multiple skin folds.
It is also more common in people who are immunocompromised and in some people taking antibiotics.
Normally, these lesions manifest on the skin as spots of red color with signs of irritation, for example, in the armpits or under the breast.
In the nails (onychomycosis) are manifested as alterations in the area of the nail that alter its appearance and normal color.
In the mucosa of the mouth or tongue infection can manifest as one or more patches of whitish, often caused by the fungus Candida albicans, knowing the condition as “thrush”.
See Also: Factors for appearance of fungi
Treatment depends on each case and each person, taking into account their clinical and personal aspects. In simple infections may be sufficient to use a cream or an ointment of an antifungal drug during a period that can range from two weeks to two months.
In other cases it is necessary to use or add topical treatment with oral medication, for example, in the case of oral candidiasis, which is necessary to take the antifungal drug in tablet form, or rather as a syrup, in order to maintain it a few minutes in the mouth or gargling, to produce a local effect, swallowing after the drug to take its pervasive effect on the body.