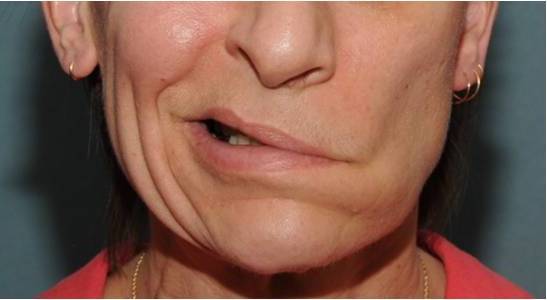
What is a facial paralysis? It is an acute syndrome that affects the facial nerve, producing weakness or temporary paralysis in the muscles of the face. It begins in the cerebral cortex, ending in the motor plates of the muscles. When an injury occurs somewhere along the path of the nerve, cerebral palsy occurs.
There are multiple causes that cause an alteration of the facial nerve. Some of them have internal origin, while others are of an external nature. Eighty percent of the cases occur without apparent cause and are best known as Bell’s palsy.
Internal causes include tumors, strokes, or cerebral vascular malformations. These can also cause head trauma, metabolic diseases, viral and bacterial infections.
What are the most common symptoms that alert you that you may have facial paralysis?
- Intense color in the facial region.
- It is established within a few hours and worsens during the first 24 to 48 hours.
- There is an asymmetry due to lack of mobility on one side of the face. You have an inability to smile normally, as well as to close the eye, alterations in tearing and speech.
- Difficulty raising the eyebrow, alterations in nasal breathing and accumulation in the back of the mouth.
- Constant drooling.
- Difficulties to smile, grimace or express facial expressions.
- Inability to eat and drink.
A facial paralysis can easily develop if you are subjected to certain everyday situations such as:
Stress: When you are exposed to worries, blood pressure increases. Stress is a way for your mind and body to react to a threat. When you suffer, you feel upset stomach, inability to concentrate, insomnia, headache, anxiety and changes in mood.
Infections: Like meningitis or the common cold, it causes the facial nerve to become inflamed, which causes heart attacks.
Migraine: The American Academy of Neurology indicates that suffering from this headache doubles the risk of this disease in the nervous system.
Diabetes: Strokes; that is to say, the interruption or the decrease in blood flow to a part of the brain due to the rupture of a blood vessel.
Cerebrovascular accident are divided into infarcts (tissue deaths) and intracerebral hemorrhage. The first is produced by tamponade of the arteries, since fats like cholesterol accumulate in the walls of the organs. And in the case of cerebrovascular accidents, it is because an artery forms a clot, which prevents blood flow.
The information provided here is not a substitute for medical advice from a specialist. If you have symptoms similar to those mentioned in this information, visit your doctor.